- HOME >
- For Researchers >
- Product Search >
- Search Result >
- #10241 Anti-Human Parkin (1A1) Mouse IgG MoAb
Product Search
#10241 Anti-Human Parkin (1A1) Mouse IgG MoAb
- Intended Use:
- Research reagents
- Application:
- WB, IP, ICC
- Package Size1:
- 100 μg
- Package Size2:
- 10 μg
- Note on Application Abbreviations
- WB:Western Blotting
- IP:Immunoprecipitation
- ICC:Immunocytochemistry
※ The product indicated as "Research reagents" in the column Intended Use cannot be used
for diagnostic nor any medical purpose.
※ The datasheet listed on this page is sample only. Please refer to the datasheet
enclosed in the product purchased before use.
Product Overview
Product Overview
| Product Code | 10241 |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Anti-Human Parkin (1A1) Mouse IgG MoAb |
| Intended Use | Research reagents |
| Application | WB, IP, ICC |
| Species | Human |
| Immunizing antigen | Synthetic peptide of the C-terminal part of human parkin (AYRVDERAAEQARWEAA) |
| Source | Mouse-Mouse hybridoma (X63 - Ag 8.653 × BALB/c mouse spleen cells, supernatant) |
| Clone Name | 1A1 |
| Subclass | IgG1 |
| Purification Method | Affinity purified with antigen peptide |
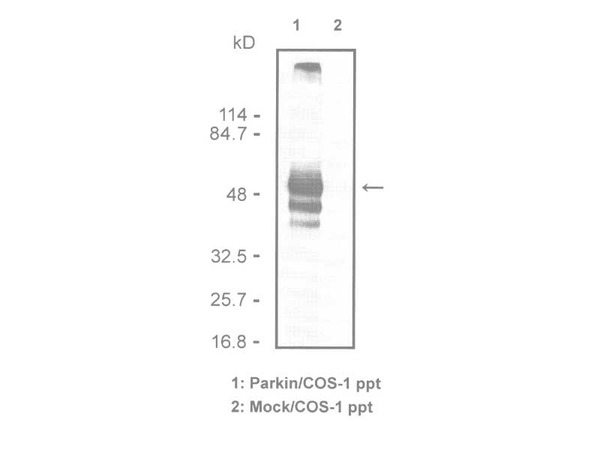
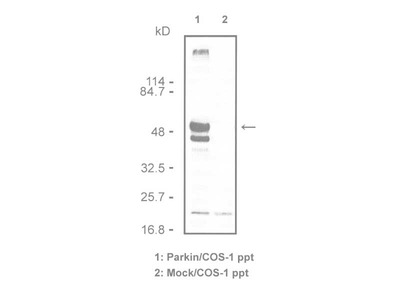
| Specificity | Specifically reacts with parkin cDNA transfected COS cells by immuno- cytochemistry. Cross-reacts with mouse and rat |
| Package Form | Lyophilized product from 1 % BSA in PBS containing 0.05 % NaN3 |
| Storage Condition | 2 - 8℃ |
| Poisonous and Deleterious Substances | Applicable |
| Cartagena | Not Applicable |
| Package Size 1 | 100 μg |
| Package Size 2 | 10 μg |
| Remarks1 | The commercial use of products without our permission is prohibited. Please make sure to contact us and obtain permission. |
Product Description
Product Description
Parkinson's Disease (PD) is a relatively common neurodegenerative disorder, which is characterized by the loss of midbrain dopamine (DA) neurons and the presence of Lewy bodies, proteinaceous cytoplasmic inclusions that are abundantly enriched in ubiquitin. It is identified a number of potential substrates for parkin, which may be involved in the pathogenesis of PD. Autosomal Recessive Juvenile Parkinsonism (AR-JP) is a recently described form of Parkinson’s Disease that has been linked to a gene that codes for parkin. Parkin, a 52 kDa protein, has a suggested role in the ubiquitin/proteasome pathway for protein degradation. The amino terminus bears sequence homology to ubiquitin while functionally it acts as a RING-type ubiquitin protein ligase (E3) that coordinates the transfer of ubiquitin to substrate proteins, thus targeting them for degradation by the proteasome.