- HOME >
- For Researchers >
- Product Search >
- Search Result >
- #10381 Anti-Human CD109 (11H3) Mouse IgG MoAb
Product Search
#10381 Anti-Human CD109 (11H3) Mouse IgG MoAb
- Intended Use:
- Research reagents
- Application:
- WB, IP, IHC
- Package Size1:
- 100 μg
- Package Size2:
- 10 μg
- Note on Application Abbreviations
- WB:Western Blotting
- IP:Immunoprecipitation
- IHC:Immunohistochemistry
※ The product indicated as "Research reagents" in the column Intended Use cannot be used
for diagnostic nor any medical purpose.
※ The datasheet listed on this page is sample only. Please refer to the datasheet
enclosed in the product purchased before use.
Product Overview
Product Overview
| Product Code | 10381 |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Anti-Human CD109 (11H3) Mouse IgG MoAb |
| Intended Use | Research reagents |
| Application | WB, IP, IHC |
| Species | Human |
| Immunizing antigen | Recombinant protein of the C-ternimal portion of Human CD109 |
| Source | Mouse-Mouse hybridoma (X63 - Ag 8.653 × BALB/c mouse spleen cells, ascites) |
| Clone Name | 11H3 |
| Subclass | IgG1 |
| Purification Method | Affinity purified with Protein A |
| Package Form | Lyophilized product from 1 % BSA in PBS containing 0.05 % NaN3 |
| Storage Condition | 2 - 8℃ |
| Poisonous and Deleterious Substances | Applicable |
| Cartagena | Not Applicable |
| Package Size 1 | 100 μg |
| Package Size 2 | 10 μg |
| Remarks1 | The commercial use of products without our permission is prohibited. Please make sure to contact us and obtain permission. |
Product Description
Product Description
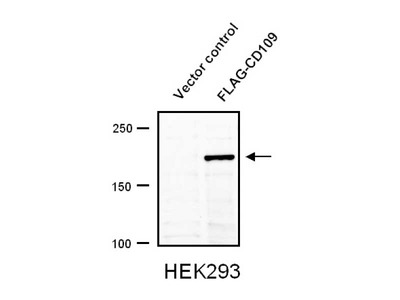
CD109 is a glycosyl-phosphatidyl-inositol (GPI) - anchored glycoprotein about 180 - 190 kDa. It is shown that CD109 is expressed in vascular endothelial cells, some epithelial cells, activated T-cells and platelets, and subset of CD34+ megakaryocytic leukemia cells. The CD109 molecules are strongly expressed in KG1a cells, while CD34+CD109+ cells in fetal bone marrow include almost all myelocytic, erythroblastec and megakaryocytic precursor cells. For this reason, CD109 is considered to be a marker of megakaryocytic hematopoiesis in early stage. And CD109 is considered different from existing activation marker of leukocyte and platelet because of its structure and serological features. By reports of Takahashi et al., CD109 is significantly over expressed in squamous cell carcinoma such as lung carcinoma, esophageal carcinoma and uterine cervical carcinoma. Thus, it is attracting attention in study of squamous cell carcinoma. Additionally, a recent study suggests that CD109 is involved in the regulation of transforming growth factor (TGF)-β signaling in some cancer cells and keratinocytes.