- HOME >
- For Researchers >
- Product Search >
- Search Result >
- #10909 Anti- CD134/OX40 (B7-B5) Mouse IgG MoAb
Product Search
#10909 Anti- CD134/OX40 (B7-B5) Mouse IgG MoAb
- Intended Use:
- Research reagents
- Application:
- WB, IP, FCM
- Package Size1:
- 500 μg
- Package Size2:
- 100 μg
- Note on Application Abbreviations
- WB:Western Blotting
- IP:Immunoprecipitation
- FCM:Flow Cytometry
※ The product indicated as "Research reagents" in the column Intended Use cannot be used
for diagnostic nor any medical purpose.
※ The datasheet listed on this page is sample only. Please refer to the datasheet
enclosed in the product purchased before use.
Product Overview
Product Overview
| Product Code | 10909 |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Anti- CD134/OX40 (B7-B5) Mouse IgG MoAb |
| Intended Use | Research reagents |
| Application | WB, IP, FCM |
| Immunizing antigen | Recombinant soluble OX40 |
| Source | Mouse-Mouse hybridoma (SP2/0 × BALB/c mouse spleen cells) |
| Clone Name | B7-B5 |
| Subclass | IgG1 |
| Purification Method | Gel filtration chromatography following ammonium sulfate precipitation |
| Package Form | Lyophilized product from PBS containing 1 % BSA and 0.05 % NaN3 |
| Storage Condition | 2 - 8℃ |
| Poisonous and Deleterious Substances | Applicable |
| Cartagena | Not Applicable |
| Package Size 1 | 500 μg |
| Package Size 2 | 100 μg |
| Remarks1 | The commercial use of products without our permission is prohibited. Please make sure to contact us and obtain permission. |
Product Description
Product Description
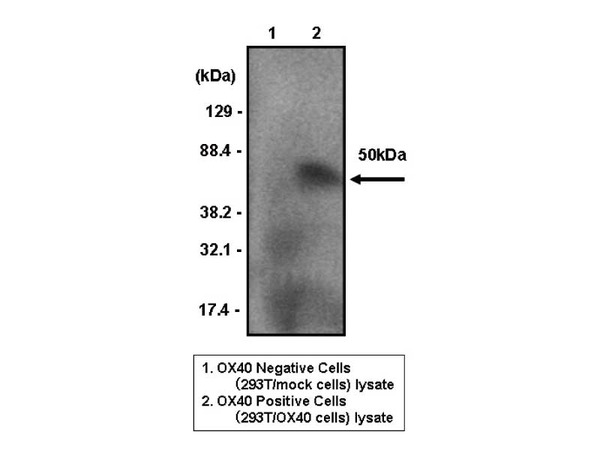
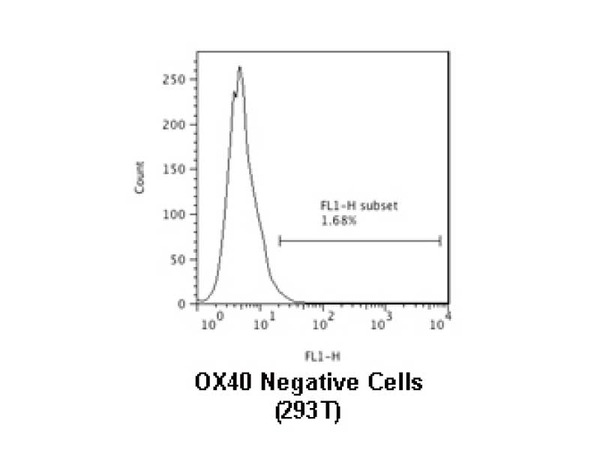
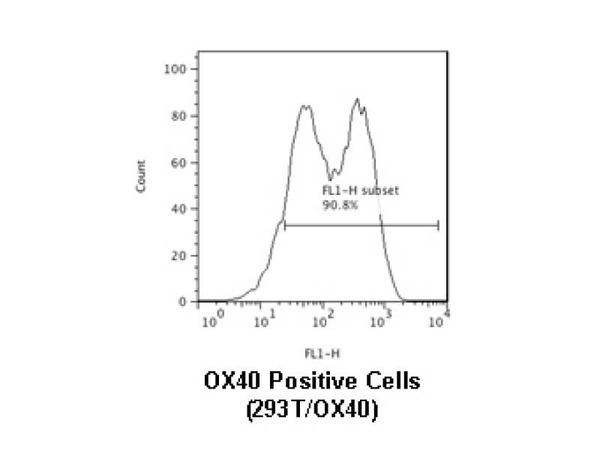
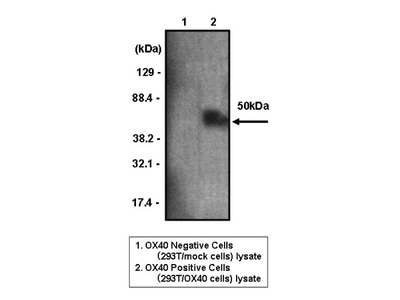
CD134/OX40 is a receptor of OX40 ligand (OX40L) transactivated by Tax of HTLV-1. OX40 is expressed in activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells. OX40 on the activated T cells have a role in proliferation of T cells and production of cytokines by binding with OX40L expressed on antigen presenting cells like dendritic cells or activated B cells. In addition, it also be involved in activated T cell invasion to inflamed area through the binding with OX40L.
FAQ
FAQ
-
 Q.Can this antibody be used for human T cell?
Q.Can this antibody be used for human T cell? -
 A.Yes, it can. This antibody was used in the following publication. Please refer to it.
A.Yes, it can. This antibody was used in the following publication. Please refer to it.
Requirements for the functional expression of OX40 ligand on human activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells.
Kondo K et al. Hum Immunol. 2007 Jul;68(7):563-71. Epub 2007 Apr 13.