- HOME >
- For Researchers >
- Product Search >
- Search Result >
- #18881 Anti-Human ERA (E. coli Ras-like protein) Rabbit IgG Affinity Purify
Product Search
#18881 Anti-Human ERA (E. coli Ras-like protein) Rabbit IgG Affinity Purify
- Intended Use:
- Research reagents
- Application:
- WB, IHC
- Package Size1:
- 100 μg
- Note on Application Abbreviations
- WB:Western Blotting
- IHC:Immunohistochemistry
※ The product indicated as "Research reagents" in the column Intended Use cannot be used
for diagnostic nor any medical purpose.
※ The datasheet listed on this page is sample only. Please refer to the datasheet
enclosed in the product purchased before use.
Product Overview
Product Overview
| Product Code | 18881 |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Anti-Human ERA (E. coli Ras-like protein) Rabbit IgG Affinity Purify |
| Intended Use | Research reagents |
| Application | WB, IHC |
| Species | Human |
| Immunizing antigen | Synthetic peptide of middle part of human ERA (E. coli Ras-like protein)((C)AVKDPNTQSVGNPQ) |
| Purification Method | Purified with antigen peptide |
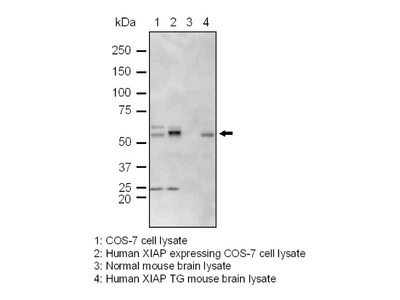
| Specificity | Confirmed by western blotting using transfectant cells |
| Package Form | Lyophilized product from 1% BSA in PBS containing 0.05% NaN3 |
| Storage Condition | 2 - 8℃ |
| Poisonous and Deleterious Substances | Applicable |
| Cartagena | Not Applicable |
| Package Size 1 | 100 μg |
| Remarks1 | The commercial use of products without our permission is prohibited. Please make sure to contact us and obtain permission. |
Product Description
Product Description
ERA (Escherichia coli Ras-like protein) is an E. coli GTP binding protein that is essential for proliferation. A DNA database search suggests that homologous sequences with ERA exist in various organisms including human, mouse, Drosophila, Caenorhabditis elegans and Antirrhinum majus. However, the physiological function of eukaryotic ERA-like proteins is not known. The human homologue has been cloned. The mammalian homologue of ERA consists of a typical GTPase/GTP-binding domain and a putative K homology (KH) domain, which is known as an RNA binding domain. Human ERA processing the amino acid substitution mutation into the GTPase domain induced apoptosis of HeLa cells, which was blocked by Bcl-2 expression. Thus, human ERA plays an important role in the regulation of apoptotic signaling with its GTPase/GTP binding domain.