- HOME >
- For Researchers >
- Product Search >
- Search Result >
- #10367 Anti-Human Reticulocalbin-1 (TMU-6A1) Mouse IgG MoAb
Product Search
#10367 Anti-Human Reticulocalbin-1 (TMU-6A1) Mouse IgG MoAb
- Intended Use:
- Research reagents
- Application:
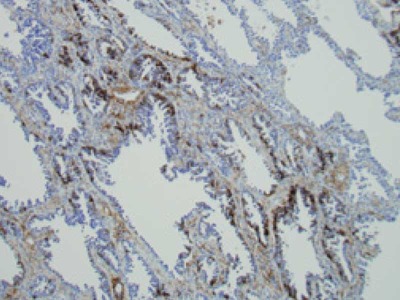
- WB, IP, IHC
- Package Size1:
- 50 μg
- Package Size2:
- 5 μg
- Note on Application Abbreviations
- WB:Western Blotting
- IP:Immunoprecipitation
- IHC:Immunohistochemistry
※ The product indicated as "Research reagents" in the column Intended Use cannot be used
for diagnostic nor any medical purpose.
※ The datasheet listed on this page is sample only. Please refer to the datasheet
enclosed in the product purchased before use.
Product Overview
Product Overview
| Product Code | 10367 |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Anti-Human Reticulocalbin-1 (TMU-6A1) Mouse IgG MoAb |
| Intended Use | Research reagents |
| Application | WB, IP, IHC |
| Species | Human |
| Immunizing antigen | Recombinant protein of the C-terminal site (90 a.a.) of human Reticulocalbin-1 |
| Source | Mouse-Mouse hybridoma (X63 - Ag 8.653 × BALB/c mouse spleen cells, supernatant) |
| Clone Name | TMU-6A1 |
| Subclass | IgG1 |
| Purification Method | Affinity purified with Protein A |
| Package Form | Lyophilized product from 1 % BSA in PBS containing 0.05 % NaN3 |
| Storage Condition | 2 - 8℃ |
| Poisonous and Deleterious Substances | Applicable |
| Cartagena | Not Applicable |
| Package Size 1 | 50 μg |
| Package Size 2 | 5 μg |
| Remarks1 | The commercial use of products without our permission is prohibited. Please make sure to contact us and obtain permission. |
Product Description
Product Description
Human Reticulocalbin-1 is a 44kDa protein and belongs to the EF (elongation factor) -hand calcium-binding protein family, and it is known as a luminal protein of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) with the C-terminal HDEL (ER retention signal) sequence. Although it is known that the protein contains six repeated domains each of which has an EF-hand motif, the function of them has not been clalified clearly. In analysis of tumor cells, higher expression of Reticulocalbin-1 is reported in hepatocellular carcinoma than normal hepatocytes and the study suggests the possibility of its involvement in malignancy of human cells through the calcium regulation, but there are few reports regarding the expression of Reticulocalbin-1 in oncology. One of the few study reports that Reticulocalubin-1 has been found to be highly expressed in cultured cells of highly invasive breast cancer, while it has not been found in low invasive cells, however, its significance is not altogether clear. One of anticancer drugs most commonly used is cisplatin. Currently, cisplatin (cis-diamminedichloroplatinum (II); cis-DDP) is a principal drug of cancer chemotherapy, and it shows beneficial effects in some solid cancers such as head and neck cancer, testicular tumor, ovary cancer and small-cell lung cancer. Hirano et al. reported that in research of markers of anticancer drug sensitivity, they compared the protein expression of cisplatin-resistant cell strains and its parent strains using the two-dimensional electrophoresis and found a spot which was markedly decreased in expression, and then, the analysis of amino acid sequence showed that the spot was Reticulocalbin-1.