- HOME >
- For Researchers >
- Product Search >
- Search Result >
- #28021 Anti- APP (Phosphorylated) Rabbit IgG Affinity Purify
Product Search
#28021 Anti- APP (Phosphorylated) Rabbit IgG Affinity Purify
- Intended Use:
- Research reagents
- Application:
- WB, IP
- Package Size1:
- 100 μg
- Package Size2:
- 10 μg
- Note on Application Abbreviations
- WB:Western Blotting
- IP:Immunoprecipitation
※ The product indicated as "Research reagents" in the column Intended Use cannot be used
for diagnostic nor any medical purpose.
※ The datasheet listed on this page is sample only. Please refer to the datasheet
enclosed in the product purchased before use.
Product Overview
Product Overview
| Product Code | 28021 |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Anti- APP (Phosphorylated) Rabbit IgG Affinity Purify |
| Intended Use | Research reagents |
| Application | WB, IP |
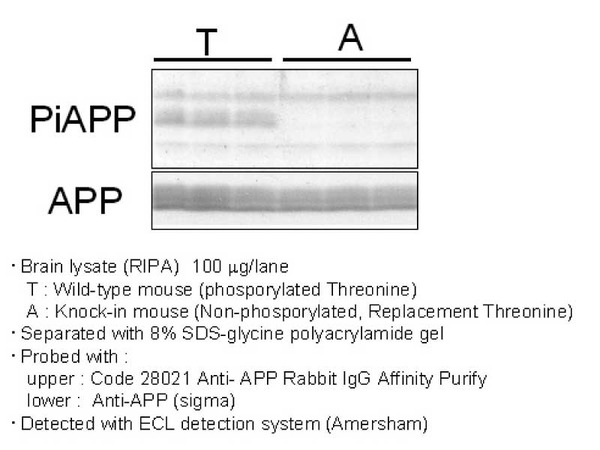
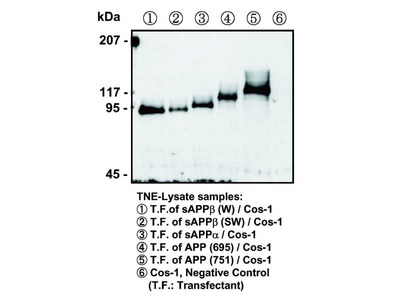
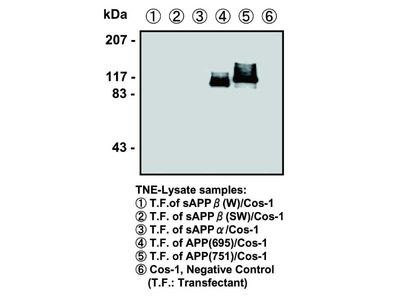
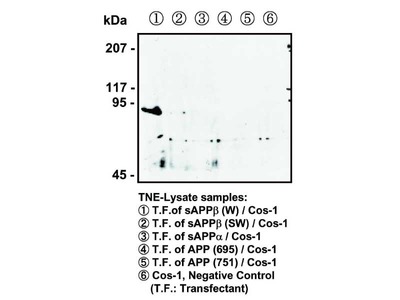
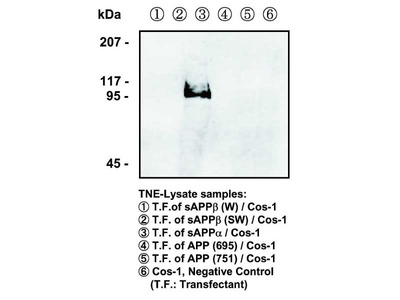
| Immunizing antigen | Synthetic peptide of Phosphorylated part of APP (DAAVpTPEE) |
| Purification Method | Purified with antigen peptide |
| Specificity | Reacts with human and mouse, and not reacts with nonphosphorylated APP. |
| Package Form | Lyophilized product from 1% BSA in PBS containing 0.05% NaN3 |
| Storage Condition | 2 - 8℃ |
| Poisonous and Deleterious Substances | Applicable |
| Cartagena | Not Applicable |
| Package Size 1 | 100 μg |
| Package Size 2 | 10 μg |
| Remarks1 | The commercial use of products without our permission is prohibited. Please make sure to contact us and obtain permission. |
Product Description
Product Description
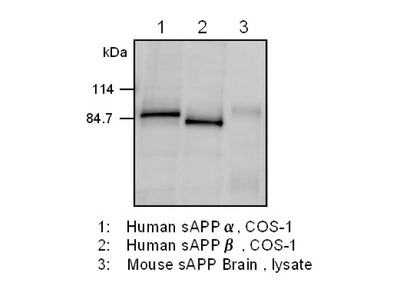
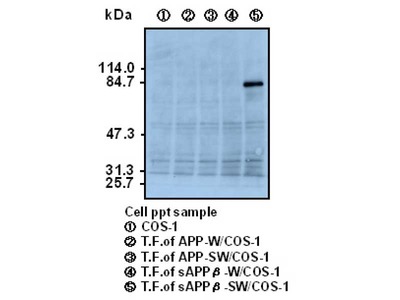
Amyloid precursor protein (APP) is precursor protein of Amyloid β which is major constituent of senile plaque in Alzheimer's disease. It is known that there are three major isoforms, APP695, APP751 and APP770, and are generated from alternative splicing of common precursor mRNA. Processing of APP occurs by two major pathways, non-amyloidogenic pathway and amyloidogenic pathway. The non-amyloidogenic pathway is mediated by α and γ-secretases and gives rise to a large fragment known as soluble APPα (sAPPα) and a small 3 kDa peptide known as p3. On the other hand, the Amyloidogenic pathway is mediated by β- and γ-secretases and yields soluble APPβ (sAPPβ) and Amyloid β. The physiologic function of APP itself is not clear, however, it is supposed that the function of APP in neuron system is different from that in other organ. Amyloidβ is derived by the sequential cleavage of amyloid precursor protein (APP) by beta- and gamma-secretases. A double missense mutation (Lys670→Asn and Met671→Leu) in APP found in a Swedish pedigree (APPβ-sw) elevates Abeta40 and Abeta42 production, and the mutation is utilized in establishment of transgenic mice overexpress a mutant form of human amyloid precursor protein. Amyloidβproduction and, beta-secretase cleavage of APPβ-sw reportedly occur in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), Golgi and endocytic compartments. In nerve cells, APP containing an N- or O-type sugar chain modification (mature APP) is phosphorylated at the Thr668 position (APP695) by the actions of Cdk5 and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase (JNK), which are nerve-specifically activated, and becomes translocated to the cell membrane and neuritis. It has been considered that the phosphorylation induces structural changes in the cytoplasmic domain of APP and influences Aβ production. Regulation of the bonding of APP with FE65 is believed to be involved in information transmission.