- HOME >
- For Researchers >
- Product Search >
- Search Result >
- #10323 Anti-Human Amyloidβ (N) (82E1) Mouse IgG MoAb
Product Search
#10323 Anti-Human Amyloidβ (N) (82E1) Mouse IgG MoAb
- Intended Use:
- Research reagents
- Application:
- WB, IP, IHC
- Package Size1:
- 50 μg
- Package Size2:
- 5 μg
- Note on Application Abbreviations
- WB:Western Blotting
- IP:Immunoprecipitation
- IHC:Immunohistochemistry
※ The product indicated as "Research reagents" in the column Intended Use cannot be used
for diagnostic nor any medical purpose.
※ The datasheet listed on this page is sample only. Please refer to the datasheet
enclosed in the product purchased before use.
Product Overview
Product Overview
| Product Code | 10323 |
|---|---|
| Product Name | Anti-Human Amyloidβ (N) (82E1) Mouse IgG MoAb |
| Intended Use | Research reagents |
| Application | WB, IP, IHC |
| Species | Human |
| Immunizing antigen | Synthetic peptide of a part of human Amyloidβ (1-16) (DAEFRHDSGYEVHHQK) |
| Source | Mouse-Mouse hybridoma (X63 - Ag 8.653 × BALB/c mouse spleen cells) |
| Clone Name | 82E1 |
| Subclass | IgG1 |
| Purification Method | Affinity purified with antigen peptide |
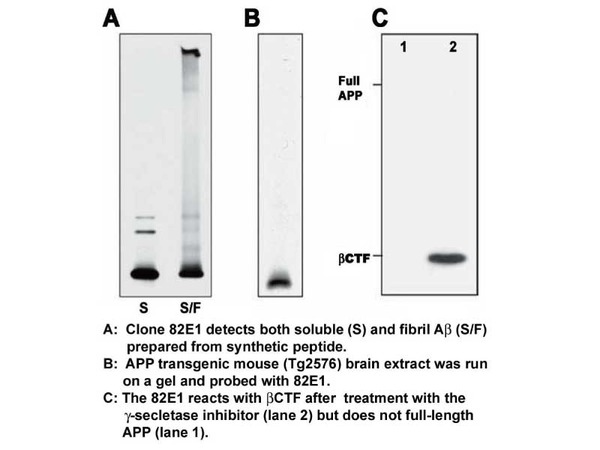
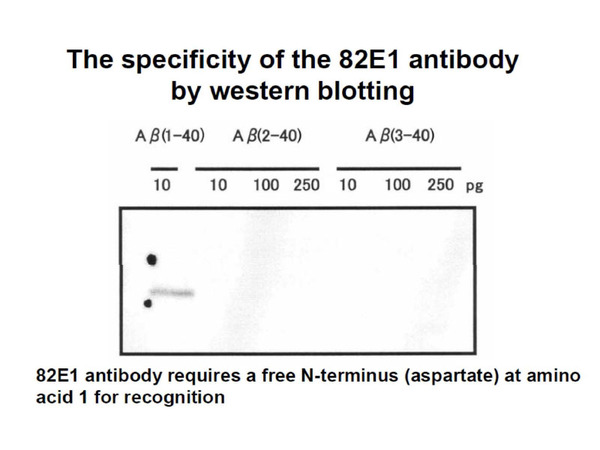
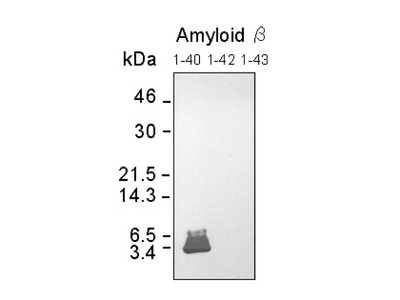
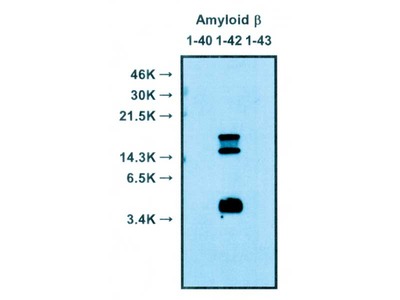
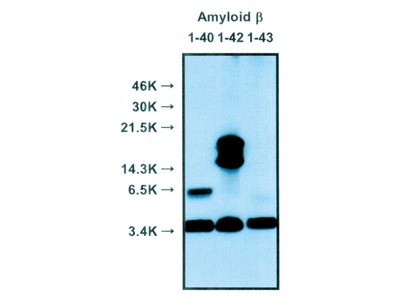
| Specificity | Human Amyloidβ N-terminal end specific. Reacts with both soluble and fibrillar Aβ at the comparable level. Not react with non-cleaved APP. |
| Package Form | Lyophilized product from PBS containing 1 % BSA and 0.05 % NaN3 |
| Storage Condition | 2 - 8℃ |
| Poisonous and Deleterious Substances | Applicable |
| Cartagena | Not Applicable |
| Package Size 1 | 50 μg |
| Package Size 2 | 5 μg |
| Remarks1 | The commercial use of products without our permission is prohibited. Please make sure to contact us and obtain permission. |
Product Description
Product Description
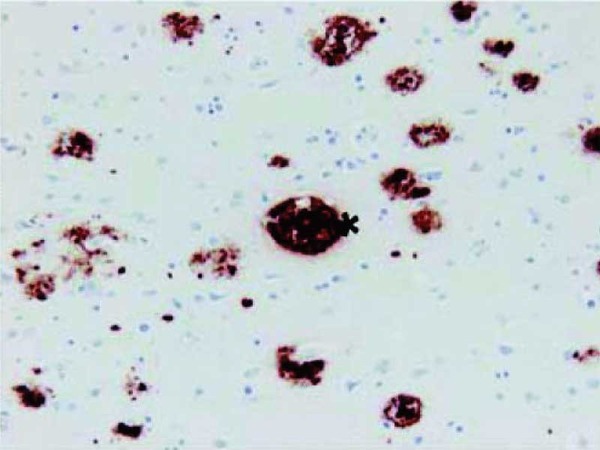
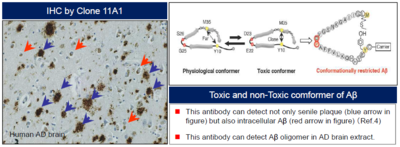
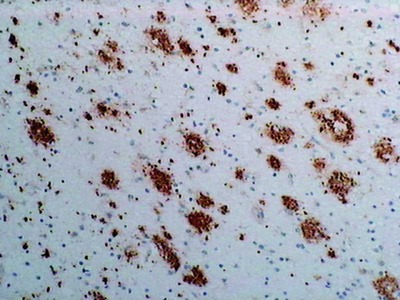
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by the presence of extracellular plaques and intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) in the brain. The major protein component of these plaques is beta amyloid (Aβ) peptide, a 40 to 43 amino acid peptide cleaved from amyloid precursor protein by β-secretase and γ-secretase. Increased release of Aβ42 or Aβ43, both of which exibit a greater tendency to aggregate than Aβ40, occurs in individuals expressing certain genetic mutations, ApoE alleles or may involve other undiscovered factors. Many researchers theorize that it is this increased release of Aβ42/Aβ43 which leads to the abnormal deposition of Aβ and the associated neurotoxicity in the brains of affected individuals. It is also reported that a distinct Aβpeptide, AβN3pE, is deposited in senile plaques in a dominant and differential manner as compared with the standard Aβpeptide.
References
References
- New Diagnostic Method for Alzheimer's Disease Based on the Toxic Conformation Theory of Amyloid β. Irie K. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2020 Jan;84(1):1-16.PMID: 31538538
- Oral Immunization with Soybean Storage Protein Containing Amyloid-β 4-10 Prevents Spatial Learning Decline. Kawarabayashi T et al. J Alzheimers Dis. 2019;70(2):487-503.PMID: 31177217
- Differential effects of diet- and genetically-induced brain insulin resistance on amyloid pathology in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Wakabayashi T et al. Mol Neurodegener. 2019 Apr 12;14(1):15.PMID: 30975165
- A Toxic Conformer of Aβ42 with a Turn at 22-23 is a Novel Therapeutic Target for Alzheimer's Disease. Izuo N et al. Sci Rep. 2017 Sep 18;7(1):11811.PMID: 28924167
- Combination therapy with octyl gallate and ferulic acid improves cognition and neurodegeneration in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Mori T et al. J Biol Chem. 2017 Jul 7;292(27):11310-11325.PMID: 28512130
- Evidence for human transmission of amyloid-β pathology and cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Jaunmuktane Z et al. Nature. 2015 Sep 10;525(7568):247-50.PMID: 26354483
- Lesion of the subiculum reduces the spread of amyloid beta pathology to interconnected brain regions in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. George S et al. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2014 Feb 11;2:17.PMID: 24517102
- Altered γ-secretase activity in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Kakuda N et al. EMBO Mol Med. 2012 Apr;4(4):344-52.PMID: 22354516
- BACE1 activity is modulated by cell-associated sphingosine-1-phosphate. Takasugi N et al. J Neurosci. 2011 May 4;31(18):6850-7.PMID: 21543615
- BACE1 inhibition reduces endogenous Abeta and alters APP processing in wild-type mice. Nishitomi K et al. J Neurochem. 2006 Dec;99(6):1555-63.PMID: 17083447
- Abeta N-terminal-end specific antibody reduced beta-amyloid in Alzheimer-model mice. Horikoshi Y et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Dec 10;325(2):384-7.PMID: 15530403
- The low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 mediates uptake of amyloid beta peptides in an in vitro model of the blood-brain barrier cells. Yamada K et al. J Biol Chem. 2008 Dec 12;283(50):34554-62.PMID: 18940800
- Development of Abeta terminal end-specific antibodies and sensitive ELISA for Abeta variant. Horikoshi Y et al. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004 Jul 2;319(3):733-7.PMID: 15184044
Note: Retrieve by PMID number in displayed by abstract: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
FAQ
FAQ
-
 Q.Does this antibody react to any APP isoform?
Q.Does this antibody react to any APP isoform? -
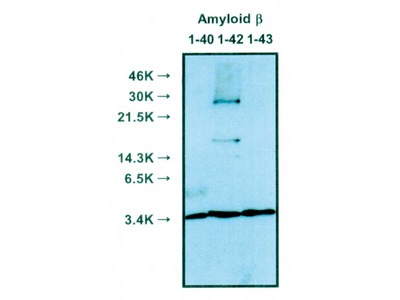
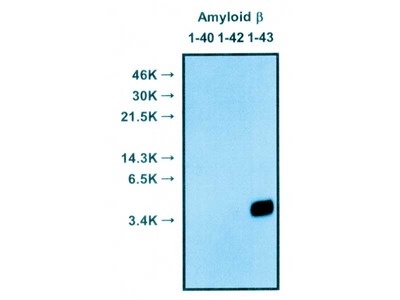
 A.As the antibody specifically reacts N-terminal of Amyloidβ, it does not react to APP, Aβ(2-40) and Aβ(3-40).
A.As the antibody specifically reacts N-terminal of Amyloidβ, it does not react to APP, Aβ(2-40) and Aβ(3-40).